目录
Date类
概述
常用方法
SimpleDateFormat类
概述
构造方法
格式规则
常用方法
Calendar类
概述
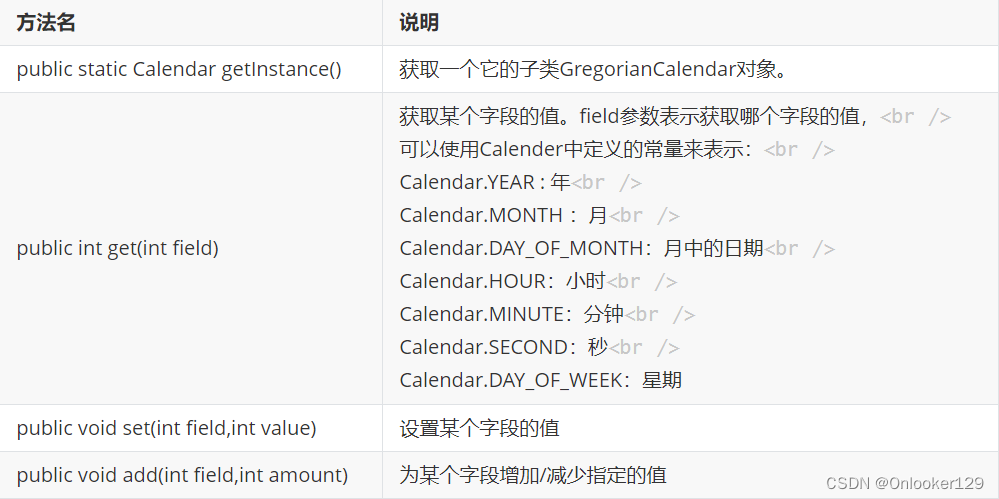
常用方法
get方法示例
set方法示例
add方法示例
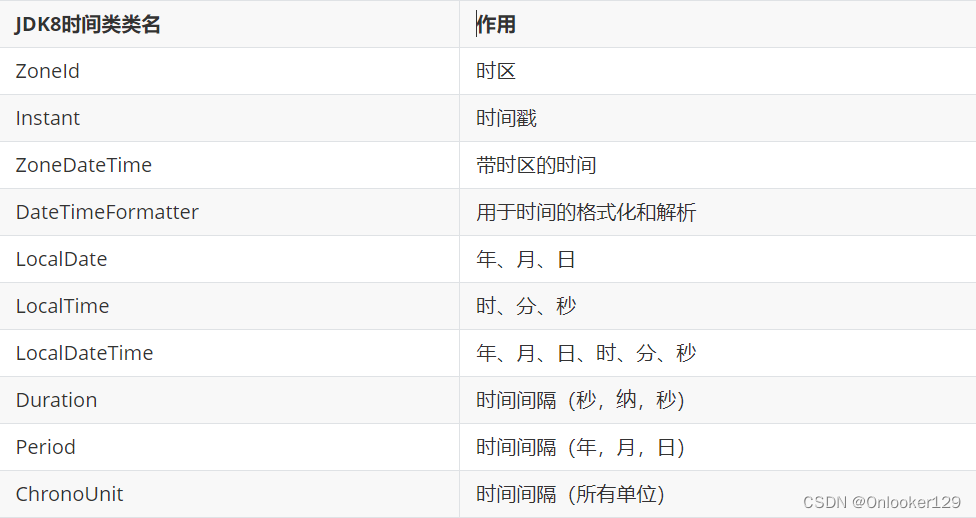
JDK8时间相关类
ZoneId 时区
Instant 时间戳
ZoneDateTime 带时区的时间
DateTimeFormatter 用于时间的格式化和解析
LocalDate 年、月、日
LocalTime 时、分、秒
LocalDateTime 年、月、日、时、分、秒
Duration 时间间隔(秒,纳秒)
Period 时间间隔(年,月,日)
ChronoUnit 时间间隔(所有单位)
包装类
概述
Integer类
概述
构造方法及静态方法
装箱和拆箱
自动装箱和自动拆箱
基本类型与字符串之间的转换
基本类型转换为String
String转换为基本类型
底层原理
练习
Date类
概述
java.util.Date类 表示特定的瞬间,精确到毫秒。
ate拥有多个构造函数,只是部分已经过时,我们重点看以下两个构造函数:
-
public Date():从运行程序的此时此刻到时间原点经历的毫秒值,转换成Date对象,分配Date对象并初始化此对象,以表示分配它的时间(精确到毫秒)。 -
public Date(long date):将指定参数的毫秒值date,转换成Date对象,分配Date对象并初始化此对象,以表示自从标准基准时间(称为“历元(epoch)”,即1970年1月1日00:00:00 GMT)以来的指定毫秒数。
tips: 由于中国处于东八区(GMT+08:00)是比世界协调时间/格林尼治时间(GMT)快8小时的时区,当格林尼治标准时间为0:00时,东八区的标准时间为08:00。
简单来说:使用无参构造,可以自动设置当前系统时间的毫秒时刻;指定long类型的构造参数,可以自定义毫秒时刻。例如:
import java.util.Date;
public class Demo01Date {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建日期对象,把当前的时间
System.out.println(new Date()); // Tue Jan 16 14:37:35 CST 2020
// 创建日期对象,把当前的毫秒值转成日期对象
System.out.println(new Date(0L)); // Thu Jan 01 08:00:00 CST 1970
}
}tips:在使用println方法时,会自动调用Date类中的toString方法。Date类对Object类中的toString方法进行了覆盖重写,所以结果为指定格式的字符串。
常用方法
-
public long getTime()把日期对象转换成对应的时间毫秒值。 -
public void setTime(long time)把方法参数给定的毫秒值设置给日期对象
示例代码:
public class DateDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建日期对象
Date d = new Date();
//public long getTime():获取的是日期对象从1970年1月1日 00:00:00到现在的毫秒值
//System.out.println(d.getTime());
//System.out.println(d.getTime() * 1.0 / 1000 / 60 / 60 / 24 / 365 + "年");
//public void setTime(long time):设置时间,给的是毫秒值
//long time = 1000*60*60;
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
d.setTime(time);
System.out.println(d);
}
}小结:Date表示特定的时间瞬间,我们可以使用Date对象对时间进行操作。
SimpleDateFormat类
概述
java.text.SimpleDateFormat 是日期/时间格式化类,我们通过这个类可以帮我们完成日期和文本之间的转换,也就是可以在Date对象与String对象之间进行来回转换。
-
格式化:按照指定的格式,把Date对象转换为String对象。
-
解析:按照指定的格式,把String对象转换为Date对象
构造方法
由于DateFormat为抽象类,不能直接使用,所以需要常用的子类java.text.SimpleDateFormat。这个类需要一个模式(格式)来指定格式化或解析的标准。构造方法为:
-
public SimpleDateFormat(String pattern):用给定的模式和默认语言环境的日期格式符号构造SimpleDateFormat。参数pattern是一个字符串,代表日期时间的自定义格式。
格式规则
常用的格式规则为:
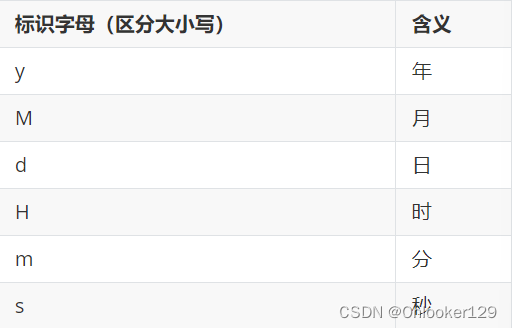
备注:更详细的格式规则,可以参考SimpleDateFormat类的API文档。
常用方法
DateFormat类的常用方法有:
-
public String format(Date date):将Date对象格式化为字符串。 -
public Date parse(String source):将字符串解析为Date对象。
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class A03_SimpleDateFormatDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
/*
public simpleDateFormat() 默认格式
public simpleDateFormat(String pattern) 指定格式
public final string format(Date date) 格式化(日期对象 ->字符串)
public Date parse(string source) 解析(字符串 ->日期对象)
*/
//1.定义一个字符串表示时间
String str = "2023-11-11 11:11:11";
//2.利用空参构造创建simpleDateFormat对象
// 细节:
//创建对象的格式要跟字符串的格式完全一致
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Date date = sdf.parse(str);
//3.打印结果
System.out.println(date.getTime());//1699672271000
}
private static void method1() {
//1.利用空参构造创建simpleDateFormat对象,默认格式
SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat();
Date d1 = new Date(0L);
String str1 = sdf1.format(d1);
System.out.println(str1);//1970/1/1 上午8:00
//2.利用带参构造创建simpleDateFormat对象,指定格式
SimpleDateFormat sdf2 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日HH:mm:ss");
String str2 = sdf2.format(d1);
System.out.println(str2);//1970年01月01日 08:00:00
//课堂练习:yyyy年MM月dd日 时:分:秒 星期
}
}
Calendar类
概述
java.util.Calendar类表示一个“日历类”,可以进行日期运算。它是一个抽象类,不能创建对象,我们可以使用它的子类:java.util.GregorianCalendar类。
有两种方式可以获取GregorianCalendar对象:
-
直接创建GregorianCalendar对象;
-
通过Calendar的静态方法getInstance()方法获取GregorianCalendar对象【使用】
常用方法
get方法示例
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取一个GregorianCalendar对象
Calendar instance = Calendar.getInstance();//获取子类对象
//2.打印子类对象
System.out.println(instance);
//3.获取属性
int year = instance.get(Calendar.YEAR);
int month = instance.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1;//Calendar的月份值是0-11
int day = instance.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
int hour = instance.get(Calendar.HOUR);
int minute = instance.get(Calendar.MINUTE);
int second = instance.get(Calendar.SECOND);
int week = instance.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);//返回值范围:1--7,分别表示:"星期日","星期一","星期二",...,"星期六"
System.out.println(year + "年" + month + "月" + day + "日" +
hour + ":" + minute + ":" + second);
System.out.println(getWeek(week));
}
//查表法,查询星期几
public static String getWeek(int w) {//w = 1 --- 7
//做一个表(数组)
String[] weekArray = {"星期日", "星期一", "星期二", "星期三", "星期四", "星期五", "星期六"};
// 索引 [0] [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
//查表
return weekArray[w - 1];
}
}
set方法示例
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//设置属性——set(int field,int value):
Calendar c1 = Calendar.getInstance();//获取当前日期
//计算班长出生那天是星期几(假如班长出生日期为:1998年3月18日)
c1.set(Calendar.YEAR, 1998);
c1.set(Calendar.MONTH, 3 - 1);//转换为Calendar内部的月份值
c1.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, 18);
int w = c1.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
System.out.println("班长出生那天是:" + getWeek(w));
}
//查表法,查询星期几
public static String getWeek(int w) {//w = 1 --- 7
//做一个表(数组)
String[] weekArray = {"星期日", "星期一", "星期二", "星期三", "星期四", "星期五", "星期六"};
// 索引 [0] [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
//查表
return weekArray[w - 1];
}
}add方法示例
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//计算200天以后是哪年哪月哪日,星期几?
Calendar c2 = Calendar.getInstance();//获取当前日期
c2.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, 200);//日期加200
int y = c2.get(Calendar.YEAR);
int m = c2.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1;//转换为实际的月份
int d = c2.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
int wk = c2.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
System.out.println("200天后是:" + y + "年" + m + "月" + d + "日" + getWeek(wk));
}
//查表法,查询星期几
public static String getWeek(int w) {//w = 1 --- 7
//做一个表(数组)
String[] weekArray = {"星期日", "星期一", "星期二", "星期三", "星期四", "星期五", "星期六"};
// 索引 [0] [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
//查表
return weekArray[w - 1];
}
}JDK8时间相关类
ZoneId 时区
/*
static Set<string> getAvailableZoneIds() 获取Java中支持的所有时区
static ZoneId systemDefault() 获取系统默认时区
static Zoneld of(string zoneld) 获取一个指定时区
*/
//1.获取所有的时区名称
Set<String> zoneIds = ZoneId.getAvailableZoneIds();
System.out.println(zoneIds.size());//600
System.out.println(zoneIds);// Asia/Shanghai
//2.获取当前系统的默认时区
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.systemDefault();
System.out.println(zoneId);//Asia/Shanghai
//3.获取指定的时区
ZoneId zoneId1 = ZoneId.of("Asia/Pontianak");
System.out.println(zoneId1);//Asia/PontianakInstant 时间戳
/*
static Instant now() 获取当前时间的Instant对象(标准时间)
static Instant ofXxxx(long epochMilli) 根据(秒/毫秒/纳秒)获取Instant对象
ZonedDateTime atZone(ZoneIdzone) 指定时区
boolean isxxx(Instant otherInstant) 判断系列的方法
Instant minusXxx(long millisToSubtract) 减少时间系列的方法
Instant plusXxx(long millisToSubtract) 增加时间系列的方法
*/
//1.获取当前时间的Instant对象(标准时间)
Instant now = Instant.now();
System.out.println(now);
//2.根据(秒/毫秒/纳秒)获取Instant对象
Instant instant1 = Instant.ofEpochMilli(0L);
System.out.println(instant1);//1970-01-01T00:00:00z
Instant instant2 = Instant.ofEpochSecond(1L);
System.out.println(instant2);//1970-01-01T00:00:01Z
Instant instant3 = Instant.ofEpochSecond(1L, 1000000000L);
System.out.println(instant3);//1970-01-01T00:00:027
//3. 指定时区
ZonedDateTime time = Instant.now().atZone(ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));
System.out.println(time);
//4.isXxx 判断
Instant instant4=Instant.ofEpochMilli(0L);
Instant instant5 =Instant.ofEpochMilli(1000L);
//5.用于时间的判断
//isBefore:判断调用者代表的时间是否在参数表示时间的前面
boolean result1=instant4.isBefore(instant5);
System.out.println(result1);//true
//isAfter:判断调用者代表的时间是否在参数表示时间的后面
boolean result2 = instant4.isAfter(instant5);
System.out.println(result2);//false
//6.Instant minusXxx(long millisToSubtract) 减少时间系列的方法
Instant instant6 =Instant.ofEpochMilli(3000L);
System.out.println(instant6);//1970-01-01T00:00:03Z
Instant instant7 =instant6.minusSeconds(1);
System.out.println(instant7);//1970-01-01T00:00:02Z
ZoneDateTime 带时区的时间
/*
static ZonedDateTime now() 获取当前时间的ZonedDateTime对象
static ZonedDateTime ofXxxx(。。。) 获取指定时间的ZonedDateTime对象
ZonedDateTime withXxx(时间) 修改时间系列的方法
ZonedDateTime minusXxx(时间) 减少时间系列的方法
ZonedDateTime plusXxx(时间) 增加时间系列的方法
*/
//1.获取当前时间对象(带时区)
ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now();
System.out.println(now);
//2.获取指定的时间对象(带时区)1/年月日时分秒纳秒方式指定
ZonedDateTime time1 = ZonedDateTime.of(2023, 10, 1,
11, 12, 12, 0, ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));
System.out.println(time1);
//通过Instant + 时区的方式指定获取时间对象
Instant instant = Instant.ofEpochMilli(0L);
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai");
ZonedDateTime time2 = ZonedDateTime.ofInstant(instant, zoneId);
System.out.println(time2);
//3.withXxx 修改时间系列的方法
ZonedDateTime time3 = time2.withYear(2000);
System.out.println(time3);
//4. 减少时间
ZonedDateTime time4 = time3.minusYears(1);
System.out.println(time4);
//5.增加时间
ZonedDateTime time5 = time4.plusYears(1);
System.out.println(time5);DateTimeFormatter 用于时间的格式化和解析
/*
static DateTimeFormatter ofPattern(格式) 获取格式对象
String format(时间对象) 按照指定方式格式化
*/
//获取时间对象
ZonedDateTime time = Instant.now().atZone(ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));
// 解析/格式化器
DateTimeFormatter dtf1=DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm;ss EE a");
// 格式化
System.out.println(dtf1.format(time));LocalDate 年、月、日
//1.获取当前时间的日历对象(包含 年月日)
LocalDate nowDate = LocalDate.now();
//System.out.println("今天的日期:" + nowDate);
//2.获取指定的时间的日历对象
LocalDate ldDate = LocalDate.of(2023, 1, 1);
System.out.println("指定日期:" + ldDate);
System.out.println("=============================");
//3.get系列方法获取日历中的每一个属性值//获取年
int year = ldDate.getYear();
System.out.println("year: " + year);
//获取月//方式一:
Month m = ldDate.getMonth();
System.out.println(m);
System.out.println(m.getValue());
//方式二:
int month = ldDate.getMonthValue();
System.out.println("month: " + month);
//获取日
int day = ldDate.getDayOfMonth();
System.out.println("day:" + day);
//获取一年的第几天
int dayofYear = ldDate.getDayOfYear();
System.out.println("dayOfYear:" + dayofYear);
//获取星期
DayOfWeek dayOfWeek = ldDate.getDayOfWeek();
System.out.println(dayOfWeek);
System.out.println(dayOfWeek.getValue());
//is开头的方法表示判断
System.out.println(ldDate.isBefore(ldDate));
System.out.println(ldDate.isAfter(ldDate));
//with开头的方法表示修改,只能修改年月日
LocalDate withLocalDate = ldDate.withYear(2000);
System.out.println(withLocalDate);
//minus开头的方法表示减少,只能减少年月日
LocalDate minusLocalDate = ldDate.minusYears(1);
System.out.println(minusLocalDate);
//plus开头的方法表示增加,只能增加年月日
LocalDate plusLocalDate = ldDate.plusDays(1);
System.out.println(plusLocalDate);
//-------------
// 判断今天是否是你的生日
LocalDate birDate = LocalDate.of(2000, 1, 1);
LocalDate nowDate1 = LocalDate.now();
MonthDay birMd = MonthDay.of(birDate.getMonthValue(), birDate.getDayOfMonth());
MonthDay nowMd = MonthDay.from(nowDate1);
System.out.println("今天是你的生日吗? " + birMd.equals(nowMd));//今天是你的生日吗?LocalTime 时、分、秒
// 获取本地时间的日历对象。(包含 时分秒)
LocalTime nowTime = LocalTime.now();
System.out.println("今天的时间:" + nowTime);
int hour = nowTime.getHour();//时
System.out.println("hour: " + hour);
int minute = nowTime.getMinute();//分
System.out.println("minute: " + minute);
int second = nowTime.getSecond();//秒
System.out.println("second:" + second);
int nano = nowTime.getNano();//纳秒
System.out.println("nano:" + nano);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
System.out.println(LocalTime.of(8, 20));//时分
System.out.println(LocalTime.of(8, 20, 30));//时分秒
System.out.println(LocalTime.of(8, 20, 30, 150));//时分秒纳秒
LocalTime mTime = LocalTime.of(8, 20, 30, 150);
//is系列的方法
System.out.println(nowTime.isBefore(mTime));
System.out.println(nowTime.isAfter(mTime));
//with系列的方法,只能修改时、分、秒
System.out.println(nowTime.withHour(10));
//plus系列的方法,只能修改时、分、秒
System.out.println(nowTime.plusHours(10));LocalDateTime 年、月、日、时、分、秒
// 当前时间的的日历对象(包含年月日时分秒)
LocalDateTime nowDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println("今天是:" + nowDateTime);//今天是:
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getYear());//年
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getMonthValue());//月
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getDayOfMonth());//日
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getHour());//时
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getMinute());//分
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getSecond());//秒
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getNano());//纳秒
// 日:当年的第几天
System.out.println("dayofYear:" + nowDateTime.getDayOfYear());
//星期
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getDayOfWeek());
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getDayOfWeek().getValue());
//月份
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getMonth());
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getMonth().getValue());
LocalDate ld = nowDateTime.toLocalDate();
System.out.println(ld);
LocalTime lt = nowDateTime.toLocalTime();
System.out.println(lt.getHour());
System.out.println(lt.getMinute());
System.out.println(lt.getSecond());Duration 时间间隔(秒,纳秒)
// 本地日期时间对象。
LocalDateTime today = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(today);
// 出生的日期时间对象
LocalDateTime birthDate = LocalDateTime.of(2000, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0);
System.out.println(birthDate);
Duration duration = Duration.between(birthDate, today);//第二个参数减第一个参数
System.out.println("相差的时间间隔对象:" + duration);
System.out.println("============================================");
System.out.println(duration.toDays());//两个时间差的天数
System.out.println(duration.toHours());//两个时间差的小时数
System.out.println(duration.toMinutes());//两个时间差的分钟数
System.out.println(duration.toMillis());//两个时间差的毫秒数
System.out.println(duration.toNanos());//两个时间差的纳秒数Period 时间间隔(年,月,日)
// 当前本地 年月日
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
System.out.println(today);
// 生日的 年月日
LocalDate birthDate = LocalDate.of(2000, 1, 1);
System.out.println(birthDate);
Period period = Period.between(birthDate, today);//第二个参数减第一个参数
System.out.println("相差的时间间隔对象:" + period);
System.out.println(period.getYears());
System.out.println(period.getMonths());
System.out.println(period.getDays());
System.out.println(period.toTotalMonths());ChronoUnit 时间间隔(所有单位)
// 当前时间
LocalDateTime today = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(today);
// 生日时间
LocalDateTime birthDate = LocalDateTime.of(2000, 1, 1,0, 0, 0);
System.out.println(birthDate);
System.out.println("相差的年数:" + ChronoUnit.YEARS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的月数:" + ChronoUnit.MONTHS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的周数:" + ChronoUnit.WEEKS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的天数:" + ChronoUnit.DAYS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的时数:" + ChronoUnit.HOURS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的分数:" + ChronoUnit.MINUTES.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的秒数:" + ChronoUnit.SECONDS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的毫秒数:" + ChronoUnit.MILLIS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的微秒数:" + ChronoUnit.MICROS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的纳秒数:" + ChronoUnit.NANOS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的半天数:" + ChronoUnit.HALF_DAYS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的十年数:" + ChronoUnit.DECADES.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的世纪(百年)数:" + ChronoUnit.CENTURIES.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的千年数:" + ChronoUnit.MILLENNIA.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的纪元数:" + ChronoUnit.ERAS.between(birthDate, today));包装类
概述
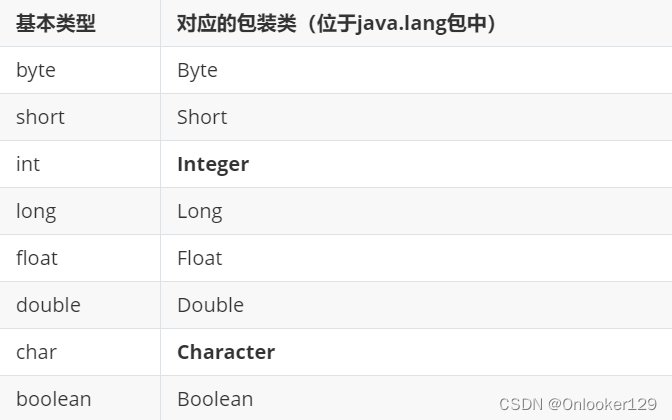
Java提供了两个类型系统,基本类型与引用类型,使用基本类型在于效率,然而很多情况,会创建对象使用,因为对象可以做更多的功能,如果想要我们的基本类型像对象一样操作,就可以使用基本类型对应的包装类,如下:
Integer类
概述
包装一个对象中的原始类型 int 的值
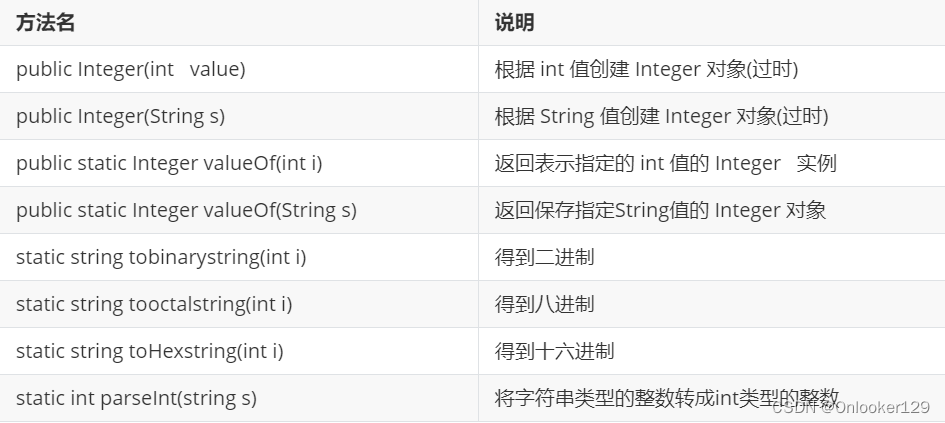
构造方法及静态方法
示例代码:
//public Integer(int value):根据 int 值创建 Integer 对象(过时)
Integer i1 = new Integer(100);
System.out.println(i1);
//public Integer(String s):根据 String 值创建 Integer 对象(过时)
Integer i2 = new Integer("100");
//Integer i2 = new Integer("abc"); //NumberFormatException
System.out.println(i2);
System.out.println("--------");
//public static Integer valueOf(int i):返回表示指定的 int 值的 Integer 实例
Integer i3 = Integer.valueOf(100);
System.out.println(i3);
//public static Integer valueOf(String s):返回保存指定String值的Integer对象
Integer i4 = Integer.valueOf("100");
System.out.println(i4);/*
public static string tobinarystring(int i) 得到二进制
public static string tooctalstring(int i) 得到八进制
public static string toHexstring(int i) 得到十六进制
public static int parseInt(string s) 将字符串类型的整数转成int类型的整数
*/
//1.把整数转成二进制,十六进制
String str1 = Integer.toBinaryString(100);
System.out.println(str1);//1100100
//2.把整数转成八进制
String str2 = Integer.toOctalString(100);
System.out.println(str2);//144
//3.把整数转成十六进制
String str3 = Integer.toHexString(100);
System.out.println(str3);//64
//4.将字符串类型的整数转成int类型的整数
//强类型语言:每种数据在java中都有各自的数据类型
//在计算的时候,如果不是同一种数据类型,是无法直接计算的。
int i = Integer.parseInt("123");
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(i + 1);//124
//细节1:
//在类型转换的时候,括号中的参数只能是数字不能是其他,否则代码会报错
//细节2:
//8种包装类当中,除了Character都有对应的parseXxx的方法,进行类型转换
String str = "true";
boolean b = Boolean.parseBoolean(str);
System.out.println(b);装箱和拆箱
基本类型与对应的包装类对象之间,来回转换的过程称为”装箱“与”拆箱“:
-
装箱:从基本类型转换为对应的包装类对象。
-
拆箱:从包装类对象转换为对应的基本类型。
用Integer与 int为例:(看懂代码即可)
基本数值---->包装对象
Integer i = new Integer(4);//使用构造函数函数
Integer iii = Integer.valueOf(4);//使用包装类中的valueOf方法包装对象---->基本数值
int num = i.intValue();自动装箱和自动拆箱
由于我们经常要做基本类型与包装类之间的转换,从Java 5(JDK 1.5)开始,基本类型与包装类的装箱、拆箱动作可以自动完成。例如:
i = i + 5;//等号右边:将i对象转成基本数值(自动拆箱) i.intValue() + 5;
//加法运算完成后,再次装箱,把基本数值转成对象。基本类型与字符串之间的转换
基本类型转换为String
转换方式
-
方式一:直接在数字后加一个空字符串
-
方式二:通过String类静态方法valueOf()
public class IntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//int --- String
int number = 100;
//方式1
String s1 = number + "";
System.out.println(s1);
//方式2
//public static String valueOf(int i)
String s2 = String.valueOf(number);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println("--------");
}
}String转换为基本类型
除了Character类之外,其他所有包装类都具有parseXxx静态方法可以将字符串参数转换为对应的基本类型:
-
public static byte parseByte(String s):将字符串参数转换为对应的byte基本类型。 -
public static short parseShort(String s):将字符串参数转换为对应的short基本类型。 -
public static int parseInt(String s):将字符串参数转换为对应的int基本类型。 -
public static long parseLong(String s):将字符串参数转换为对应的long基本类型。 -
public static float parseFloat(String s):将字符串参数转换为对应的float基本类型。 -
public static double parseDouble(String s):将字符串参数转换为对应的double基本类型。 -
public static boolean parseBoolean(String s):将字符串参数转换为对应的boolean基本类型。
代码使用(仅以Integer类的静态方法parseXxx为例)如:
转换方式
-
方式一:先将字符串数字转成Integer,再调用valueOf()方法
-
方式二:通过Integer静态方法parseInt()进行转换
public class IntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//String --- int
String s = "100";
//方式1:String --- Integer --- int
Integer i = Integer.valueOf(s);
//public int intValue()
int x = i.intValue();
System.out.println(x);
//方式2
//public static int parseInt(String s)
int y = Integer.parseInt(s);
System.out.println(y);
}
}注意:如果字符串参数的内容无法正确转换为对应的基本类型,则会抛出java.lang.NumberFormatException异常。
底层原理
建议:获取Integer对象的时候不要自己new,而是采取直接赋值或者静态方法valueOf的方式
因为在实际开发中,-128~127之间的数据,用的比较多。如果每次使用都是new对象,那么太浪费内存了。
所以,提前把这个范围之内的每一个数据都创建好对象,如果要用到了不会创建新的,而是返回已经创建好的对象。
//1.利用构造方法获取Integer的对象(JDK5以前的方式)
/*Integer i1 = new Integer(1);
Integer i2 = new Integer("1");
System.out.println(i1);
System.out.println(i2);*/
//2.利用静态方法获取Integer的对象(JDK5以前的方式)
Integer i3 = Integer.valueOf(123);
Integer i4 = Integer.valueOf("123");
Integer i5 = Integer.valueOf("123", 8);
System.out.println(i3);
System.out.println(i4);
System.out.println(i5);
//3.这两种方式获取对象的区别(掌握)
//底层原理:
//因为在实际开发中,-128~127之间的数据,用的比较多。
//如果每次使用都是new对象,那么太浪费内存了
//所以,提前把这个范围之内的每一个数据都创建好对象
//如果要用到了不会创建新的,而是返回已经创建好的对象。
Integer i6 = Integer.valueOf(127);
Integer i7 = Integer.valueOf(127);
System.out.println(i6 == i7);//true
Integer i8 = Integer.valueOf(128);
Integer i9 = Integer.valueOf(128);
System.out.println(i8 == i9);//false
//因为看到了new关键字,在Java中,每一次new都是创建了一个新的对象
//所以下面的两个对象都是new出来,地址值不一样。
/*Integer i10 = new Integer(127);
Integer i11 = new Integer(127);
System.out.println(i10 == i11);
Integer i12 = new Integer(128);
Integer i13 = new Integer(128);
System.out.println(i12 == i13);*/
练习
1.
需求:
键盘录入一些1~10日之间的整数,并添加到集合中。直到集合中所有数据和超过200为止。
代码示例:
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
键盘录入一些1~10日之间的整数,并添加到集合中。直到集合中所有数据和超过200为止。
*/
//1.创建一个集合用来添加整数
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
//2.键盘录入数据添加到集合中
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入一个整数");
String numStr = sc.nextLine();
int num = Integer.parseInt(numStr);//先把异常数据先进行过滤
if (num < 1 || num > 100){
System.out.println("当前数字不在1~100的范围当中,请重新输入");
continue;
}
//添加到集合中//细节:
//num:基本数据类型
//集合里面的数据是Integer
//在添加数据的时候触发了自动装箱
list.add(num);
//统计集合中所有的数据和
int sum = getSum(list);
//对sum进行判断
if(sum > 200){
System.out.println("集合中所有的数据和已经满足要求");
break;
}
}
}
private static int getSum(ArrayList<Integer> list) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
//i :索引
//list.get(i);
int num = list.get(i);
sum = sum + num;//+=
}
return sum;
}
}
2.
需求:
自己实现parseInt方法的效果,将字符串形式的数据转成整数。要求:字符串中只能是数字不能有其他字符最少一位,最多10位日不能开头
代码示例:
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
自己实现parseInt方法的效果,将字符串形式的数据转成整数。要求:
字符串中只能是数字不能有其他字符最少一位,最多10位日不能开头
*/
//1.定义一个字符串
String str = "123";
//2.校验字符串
//习惯:会先把异常数据进行过滤,剩下来就是正常的数据。
if (!str.matches("[1-9]\\d{0,9}")) {
//错误的数据
System.out.println("数据格式有误");
} else {
//正确的数据
System.out.println("数据格式正确");
//3.定义一个变量表示最终的结果
int number = 0;
//4.遍历字符串得到里面的每一个字符
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
int c = str.charAt(i) - '0';//把每一位数字放到number当中
number = number * 10 + c;
}
System.out.println(number);
System.out.println(number + 1);
}
}
}3.
需求:
定义一个方法自己实现toBinaryString方法的效果,将一个十进制整数转成字符串表示的二进制
代码示例:
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
定义一个方法自己实现toBinaryString方法的效果,将一个十进制整数转成字符串表示的二进制
*/
}
public static String tobinarystring(int number) {//6
//核心逻辑:
//不断的去除以2,得到余数,一直到商为日就结束。
//还需要把余数倒着拼接起来
//定义一个StringBuilder用来拼接余数
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
//利用循环不断的除以2获取余数
while (true) {
if (number == 0) {
break;
}
//获取余数 %
int remaindar = number % 2;//倒着拼接
sb.insert(0, remaindar);
//除以2 /
number = number / 2;
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
4.
需求:
请使用代码实现计算你活了多少天,用JDK7和JDK8两种方式完成
代码示例:
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
//请使用代码实现计算你活了多少天,用JDK7和JDK8两种方式完成
//JDK7
//规则:只要对时间进行计算或者判断,都需要先获取当前时间的毫秒值
//1.计算出生年月日的毫秒值
String birthday = "2000年1月1日";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日");
Date date = sdf.parse(birthday);
long birthdayTime = date.getTime();
//2.获取当前时间的毫秒值
long todayTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//3.计算间隔多少天
long time = todayTime - birthdayTime;
System.out.println(time / 1000 / 60 / 60 / 24);
//JDK8
LocalDate ld1 = LocalDate.of(2000, 1, 1);
LocalDate ld2 = LocalDate.now();
long days = ChronoUnit.DAYS.between(ld1, ld2);
System.out.println(days);
}
}5.
需求:
判断任意的一个年份是闰年还是平年要求:用JDK7和JDK8两种方式判断提示:二月有29天是闰年一年有366天是闰年
代码示例:
public class Test5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
判断任意的一个年份是闰年还是平年要求:用JDK7和JDK8两种方式判断提示:
二月有29天是闰年一年有366天是闰年
*/
//jdk7
//我们可以把时间设置为2000年3月1日
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
c.set(2000, 2, 1);
//月份的范围:0~11
//再把日历往前减一天
c.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, -1);
//看当前的时间是28号还是29号?
int day = c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
System.out.println(day);
//jdk8
//月份的范围:1~12
//设定时间为2000年的3月1日
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.of(2001, 3, 1);
//把时间往前减一天
LocalDate ld2 = ld.minusDays(1);
//获取这一天是一个月中的几号
int day2 = ld2.getDayOfMonth();
System.out.println(day2);
//true:闰年
//false:平年
System.out.println(ld.isLeapYear());
}
}![摸鱼大数据——Spark基础——Spark环境安装——Spark Local[*]搭建](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/c027155d833b4b0c90a33e2ee1e08a65.png)